 The Accent (Part two)
The Accent (Part two)
The third circumstance of the 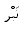 in recitation
in recitation
This occurs when changing over
from a medd letter to the first letter of a shaddah. The saakin letter occurs
with ![]() and the mouth
was busy emitting the lengthened letter, so then it is necessary at the change
over from the medd to the saakin letter that occurs after it, we put an accent
(
and the mouth
was busy emitting the lengthened letter, so then it is necessary at the change
over from the medd to the saakin letter that occurs after it, we put an accent
( ![]() ) in our recital to facilitate this change
over. This
) in our recital to facilitate this change
over. This ![]() allows us to comply with reciting the
saakin letter with
allows us to comply with reciting the
saakin letter with ![]() (with collision)
that leaves an acoustical mark. The saakin letter then makes its presence
known quite clearly. If the
(with collision)
that leaves an acoustical mark. The saakin letter then makes its presence
known quite clearly. If the ![]() (collision) is
weak the letter is then pronounced with a weak sound to such a degree that it
may not even be heard. This is often heard from some people when they recite
(collision) is
weak the letter is then pronounced with a weak sound to such a degree that it
may not even be heard. This is often heard from some people when they recite
![]() , with one
, with one ![]() with a kasrah on it instead of the two
written
with a kasrah on it instead of the two
written ![]() , the first saakinah, the second with a
vowel; this mistake of pronouncing only one
, the first saakinah, the second with a
vowel; this mistake of pronouncing only one ![]() is due to not making the
is due to not making the ![]() . Other examples of this the third
circumstance of the
. Other examples of this the third
circumstance of the ![]() are in:
are in:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Click here to listen to this word with the
Click here to listen to this word with the ![]()
![]() Click here to listen to this word with the
Click here to listen to this word with the ![]()
In all these cases there is a medd letter followed by a shaddah, and we need to make an accent, or raise our voices slightly at the end of the medd, to make sure we pronounce both parts of the shaddah, the saakin letter and voweled letter.
The Fourth circumstance of  in recitation of the Glorious Qur’an
in recitation of the Glorious Qur’an
This occurs when stopping
on a word that has a hamzah as the last letter preceded by a medd letter or
leen letter. The reason for ![]() here is so that the hamzah is not lost
after the mouth was busy emitting the medd or leen letter. Remember, we do not
stop on the hamzah with a sukoon when there is a tanween with a fathah on the
hamzah when it is the last letter of the word; instead we stop with a
here is so that the hamzah is not lost
after the mouth was busy emitting the medd or leen letter. Remember, we do not
stop on the hamzah with a sukoon when there is a tanween with a fathah on the
hamzah when it is the last letter of the word; instead we stop with a ![]() , so there would be no
, so there would be no ![]() then.
then.
Examples:
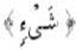
![]()
![]()
![]()
The Fifth circumstance of  in recitation of the Glorious Qur’an
in recitation of the Glorious Qur’an
This circumstance encompasses three different words in three
specific locations in the Qur’an, when these words are read in continuation
with the following word. These three words are all past tense verbs in the
double form of the verb (which is an alif) followed by a sukoon. The ![]() is needed in these three places so the
meaning of the verse is not confused. The
is needed in these three places so the
meaning of the verse is not confused. The ![]() is an indication that there is an alif
indicating a double present, but it was dropped in pronunciation due to the
Arabic rule forbidding two saakin juxtaposed letters to be recited together.
Without the
is an indication that there is an alif
indicating a double present, but it was dropped in pronunciation due to the
Arabic rule forbidding two saakin juxtaposed letters to be recited together.
Without the ![]() , the listener may think the verb is male
singular instead of male double. The
, the listener may think the verb is male
singular instead of male double. The ![]() is used only when reciting these words in
continuum with the next word, when stopping on the verbs the alif indicating a
double is then pronounced because there is no longer the meeting of two saakin
letters and there is no need for the
is used only when reciting these words in
continuum with the next word, when stopping on the verbs the alif indicating a
double is then pronounced because there is no longer the meeting of two saakin
letters and there is no need for the ![]() since the reason for it has disappeared.
since the reason for it has disappeared.
![]()
![]()
![]()